Improving Traumatic Brain Injury Through Supplements & Diet
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) remains a major concern for athletes, military personnel, and individuals involved in accidents. While advancements in protective gear and medical interventions have improved outcomes, research is increasingly focused on non-invasive strategies to mitigate the effects of TBI. A recent review by Conti et al. (2024) sheds light on the potential of dietary protocols and supplementation in supporting brain health and recovery following TBI.
The Role of Nutrition in Brain Health
The brain is highly metabolically active, relying on a consistent supply of nutrients to maintain optimal function and repair mechanisms. Following a TBI, there is an increased demand for energy and nutrients to facilitate healing, reduce inflammation, and restore neural connectivity. In their review, Conti and colleagues emphasize that proper nutrition, both before and after injury, plays a critical role in supporting brain recovery and resilience.
Key Nutrients and Supplements for TBI Recovery
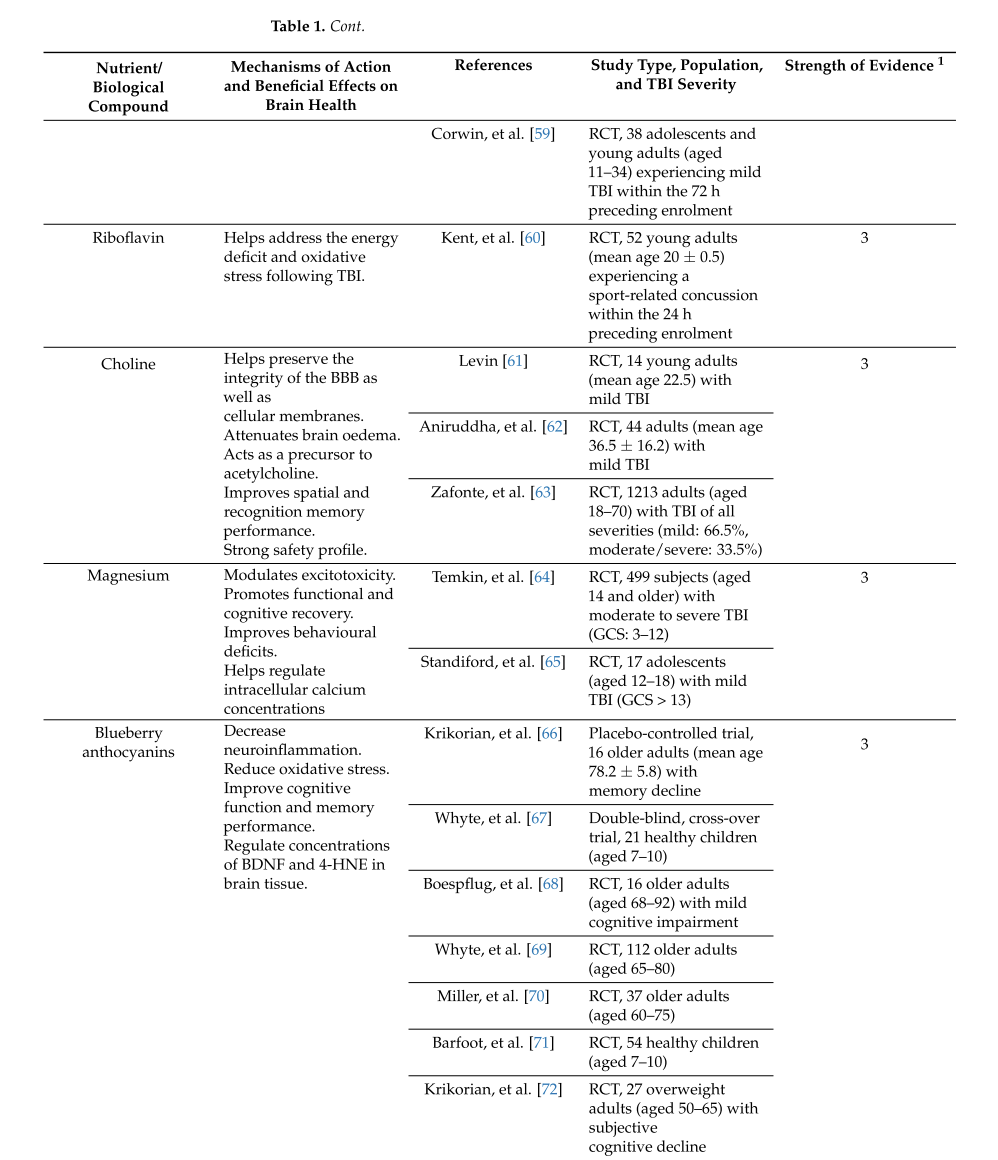
The study outlines several key nutrients and supplements that have shown promise in mitigating the impact of TBI:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA & EPA): Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fish oils, are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They are vital for maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes in the brain. Conti et al. highlight that supplementing with omega-3s may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress following a TBI, promoting quicker recovery of cognitive and motor functions.
Creatine: Traditionally used to enhance muscle strength and endurance, creatine has recently gained attention for its neuroprotective properties. According to the review, creatine may help stabilize cellular energy metabolism and reduce the extent of neuronal damage post-TBI by supporting ATP production, the primary energy currency of the cell.
Curcumin: Derived from the spice turmeric, curcumin is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound. Conti and colleagues note that curcumin may help reduce neuroinflammation and promote neuronal repair mechanisms in the aftermath of a TBI. However, due to its low bioavailability, the use of bioenhanced formulations is recommended.
Magnesium: Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of neuronal cell membranes. The review points out that magnesium deficiency following TBI may exacerbate excitotoxicity (neuronal damage caused by excessive stimulation), so supplementation can be beneficial in limiting further damage and improving cognitive recovery.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is not only essential for bone health but also for brain function. The review suggests that maintaining optimal vitamin D levels could reduce the risk of neuroinflammation and support overall brain resilience after a traumatic injury.
Review Table 1 & Table 2 below for information on additional supplements.
Conclusion
The narrative review by Conti et al. (2024) offers compelling evidence for the role of targeted supplementation and dietary protocols in mitigating the effects of TBI. By incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, creatine, curcumin, magnesium, and vitamin D into recovery protocols, along with dietary strategies like the ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting, individuals with TBI may experience improved outcomes. As research in this area continues to evolve, these nutritional strategies hold promise for enhancing the body’s ability to recover from traumatic brain injuries.
References: Conti, F., McCue, J. J., DiTuro, P., Galpin, A. J., & Wood, T. R. (2024). Mitigating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Review of Supplementation and Dietary Protocols. Nutrients, 16(15), 2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU16152430